Products
Products
[Basic Knowledge about Cryopumps 5 ]
Principle of Refrigerator Operation
1.Principle of Refrigeration
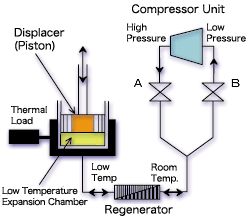 |
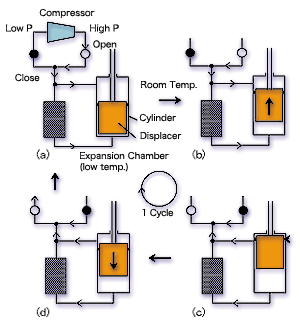
| Figure 1.Principle of Refrigeration |
2.Refrigeration Cycle for Cryopumps
Two types of refrigeration cycle for cryopumps operation are in common use: the Gifford-McMahon cycle(G-M cycle) and the Modified-Solvay cycle(M-Solvay cycle). G-M cycle ensures more reliable operation, thus becomes much popular for cryopumps refrigeration cycle.
ULVAC CRYOGENICS employs G-M cycle refrigerator for CRYO-U cryopumps.
2-1.G-M(Gifford-McMahon) Cycle
G-M cycle was developed by Gifford in the late 1950’s. The displacer in this refrigeration cycle are usually mechanically driven, or pneumatically driven. G-M cycle is very efficient and reliable refrigeration cycle which operates at slow speed and gives a little damage to the seal used inside refrigerator. In this manual, the mechanical driven refrigeration cycle used in CRYO-U® cryopumps will be explained.
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
|
|
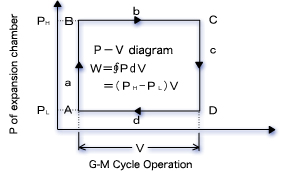
As shown in Fig. 2, the ideal P-V diagram of G-M cycle shows a square pattern.
Ideal refrigerating capacity (Q ideal) is given by the following equation where the period of one cycle is taken at t second, Q ideal = W/t
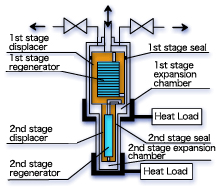
The actual refrigerator has two stage construction to achieve extreme low temperature below 15K. Also, for cryopumps, usually the regenerator is placed inside the displacer for simplification. Two stage refrigerator is designed to reduce a load to 1st and 2nd seals with differential pressure so that it performs long-period, highly reliable operation.